java代码审计
java 代码审计整理,目录如下
一、sql注入
二、命令执行
三、文件上传
四、xss
五、目录遍历
六、CSRF
七、XXE
八、SSRF
九、url跳转
十、不安全反序列化
十一、fastjson
十二、log4j
十三、未授权
十四、代码审计实战
一、sql注入
1、通过一些关键字可以定位到SQL语句附近
Statement
createStatement
PrepareStatement
like '%${
in (${
select
update
insert
(一)、JDBC的SQL注入
1、常规漏洞
实操–搭建springboot
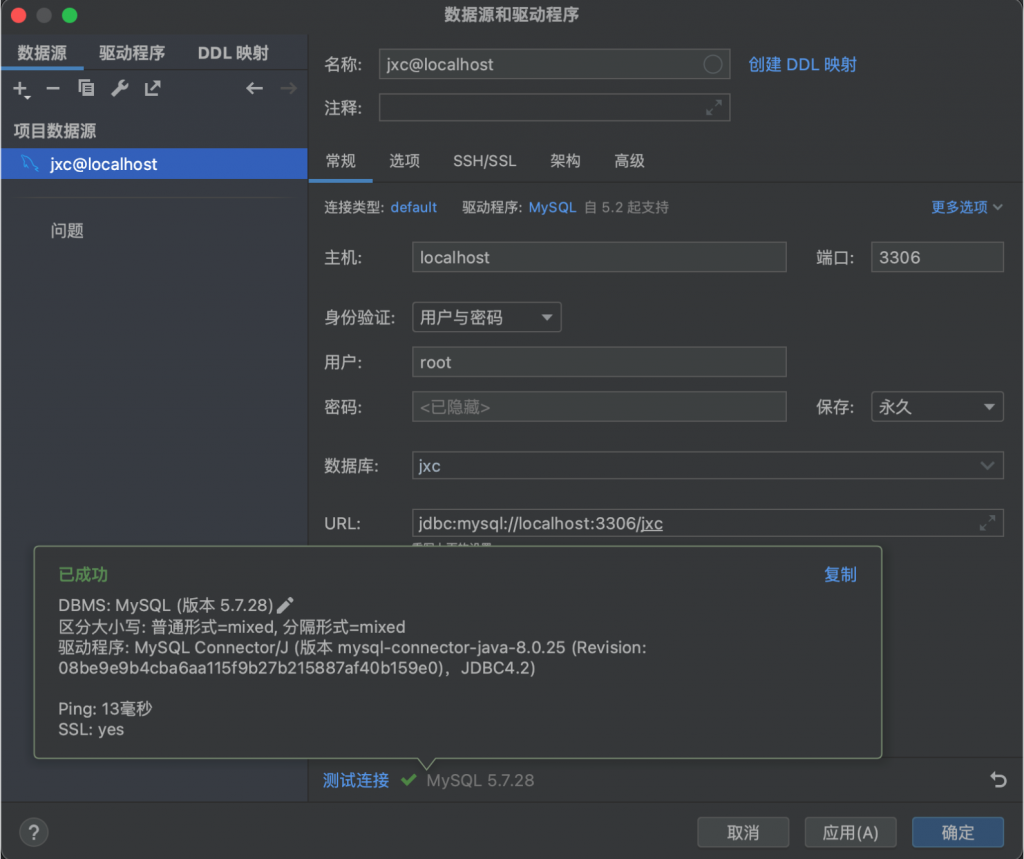
配置数据库
打开 src/main/resources/application.properties 配置文件,将以下数据库连接信息添加至配置中
#访问端口号
server.port=7070
#数据库连接信息
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java_sec-code?AllowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
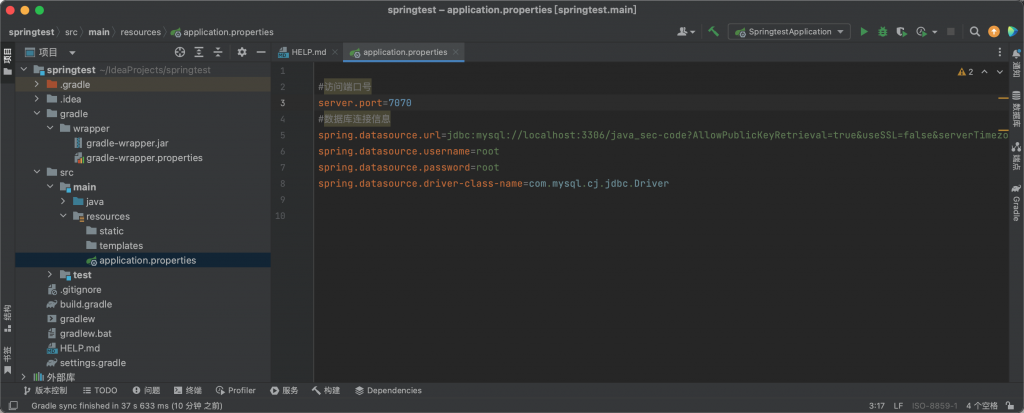
在 src\main\java\com\example\demo\jdbcinjection 下新建一个名为 JdbcDynamicController 的 Java Class。
package com.example.sql.jdbc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.sql.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/jdbcsql")
public class JdbcDynamicController {
private static String driver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
//使用的是MySQL数据库的JDBC驱动,其类名是 "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"。这个驱动类负责与MySQL数据库建立连接。
//用于从配置文件中读取属性值
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String user_name;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
@RequestMapping("/dynamic")
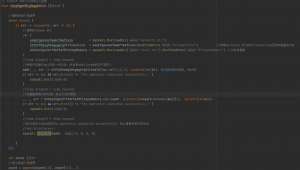
public String jdbcdynamic(@RequestParam("id") String id) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user_name, password);
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from user where user_id = '" + id + "'";
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//遍历结果集
while (rs.next()) {
String rsUsername = rs.getString("user_name");
String rsPassword = rs.getString("password");
String info = String.format("%s: %s\n", rsUsername, rsPassword);
result.append(info);
}
rs.close();
conn.close();
return result.toString();
}
}
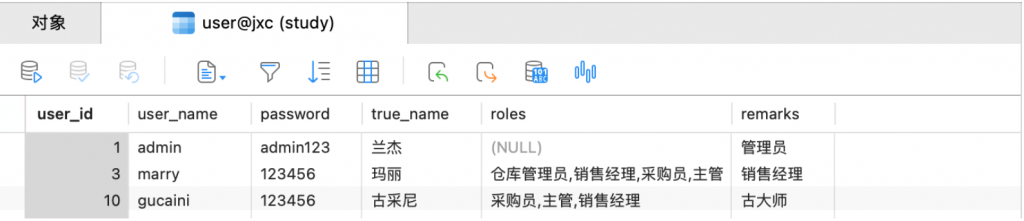
测试
http://127.0.0.1:7070/jdbcsql/dynamic?id=3
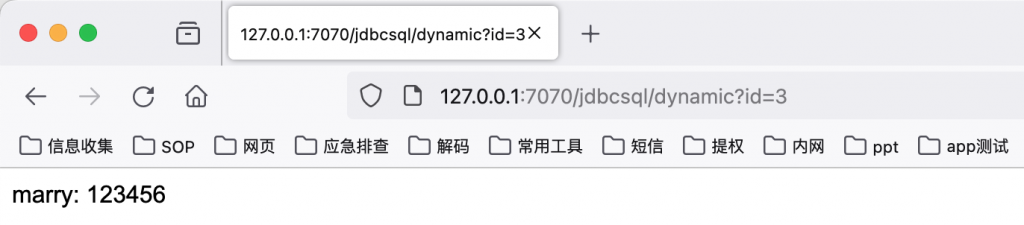
漏洞修复
在 src\main\java\com\example\demo\jdbcinjection 下新建一个名为 JdbcPrepareStatement 的 Java Class
package com.example.sql.jdbc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.sql.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/jdbcsqld")
public class JdbcPrepareStatement {
private static String driver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String user_name;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
@RequestMapping("/preSec")
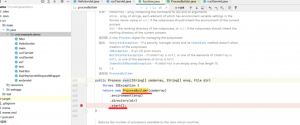
public String jdbcPreSec(@RequestParam("id") String id) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
if (id == null || id.trim().isEmpty()) {
return "Invalid id";
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
try {
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user_name, password);
String sql = "select * from user where user_id=?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, id);
ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String resUsername = rs.getString("user_name");
String resPassword = rs.getString("password");
String info = String.format("%s: %s\n", resUsername, resPassword);
result.append(info);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// Log or handle the exception here
return "Error occurred: " + e.getMessage();
}
return result.toString();
}
@RequestMapping("/preNot")
public String jdbcPreNot(@RequestParam("id") String id) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user_name, password);
//还是直接进行了拼接 无效
String sql = "select * from user where user_id = '" + id + "'";
PreparedStatement preparestatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = preparestatement.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String reUsername = rs.getString("user_name");
String resPassword = rs.getString("password");
String info = String.format("%s: %s\n", reUsername, resPassword);
result.append(info);
}
rs.close();
conn.close();
return result.toString();
}
}
正确的预编译代码效果:
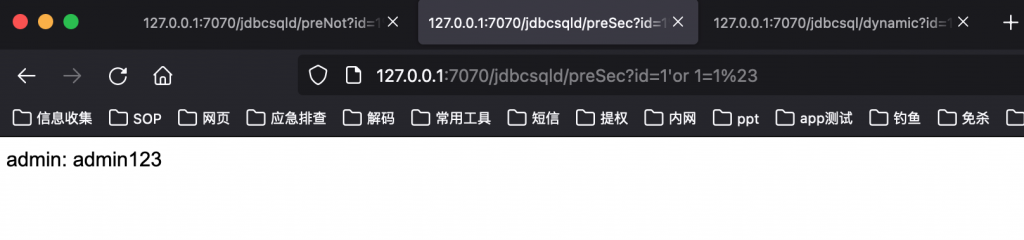
http://127.0.0.1:7070/jdbcsqld/preNot?id=1%27or%201=1%23
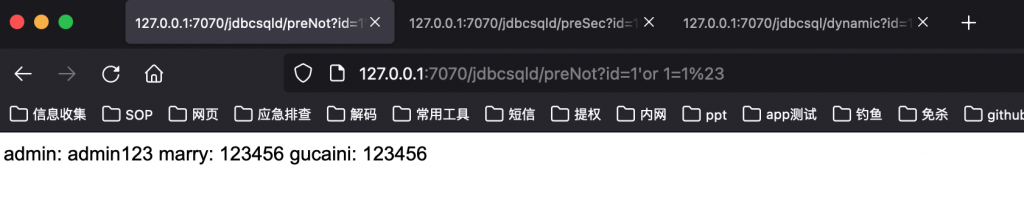
错误的预编译代码效果:
http://127.0.0.1:7070/jdbcsqld/preSec?id=1%27or%201=1%23
2、order by注入
order by 语句用于对结果集进行排序。 order by 语句后面需要是字段名或者字段位 置。 在使用 PreparedStatement 预编译时,会将传递任意参数使用单引号包裹进而变为了字符串。 如果使用预编译方式执行 order by 语句,设置的字段名会被人为是字符串,而不再是字段名。 因此,在使用 order by 时,就不能使用 PreparedStatement 预编译了
新建一个名为 jdbcOrderby 的Java Class, 并键入以下代码
package com.example.sql.jdbc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.sql.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/jdbcsqlorderby")
public class jdbcOrderby {
private static String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String user_name;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
@RequestMapping("/PreOrderby")
public String jdbcOrderby(@RequestParam("id") String id) throws
ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user_name, password);
String sql = "select * from user" + " order by " + id;
PreparedStatement preparestatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = preparestatement.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String reUsername = rs.getString("user_name");
String resPassword = rs.getString("password");
String info = String.format("%s: %s\n", reUsername, resPassword);
result.append(info);
}
rs.close();
conn.close();
return result.toString();
}
}
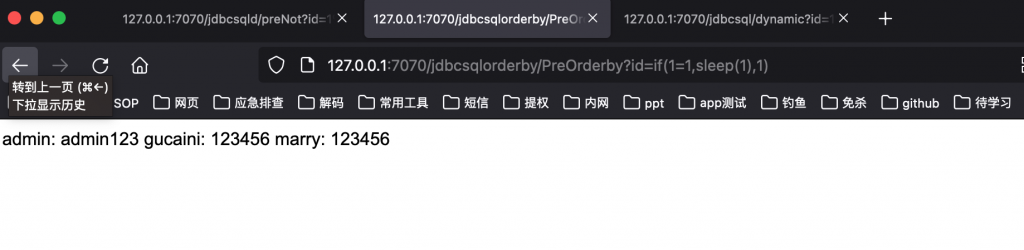
测试
http://127.0.0.1:7070/jdbcsqlorderby/PreOrderby?id=if(1=1,sleep(1),1)
漏洞修复
package com.example.sql.jdbc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.sql.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/jdbcsqlorderbysec")
public class jdbcOrderbysec {
private static String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String user_name;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
@RequestMapping("/PreOrderbysec")
public String jdbcOrderby(@RequestParam("id") String id) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
String sql = "select * from user order by ?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user_name, password);
PreparedStatement preparestatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparestatement.setString(1, id);
ResultSet rs = preparestatement.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String reUsername = rs.getString("user_name");
String resPassword = rs.getString("password");
String info = String.format("%s: %s\n", reUsername, resPassword);
result.append(info);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); // or log the exception
// Handle the SQL exception appropriately
return "Error occurred: " + e.getMessage();
}
return result.toString();
}
}
使用 PreparedStatement来安全地处理参数
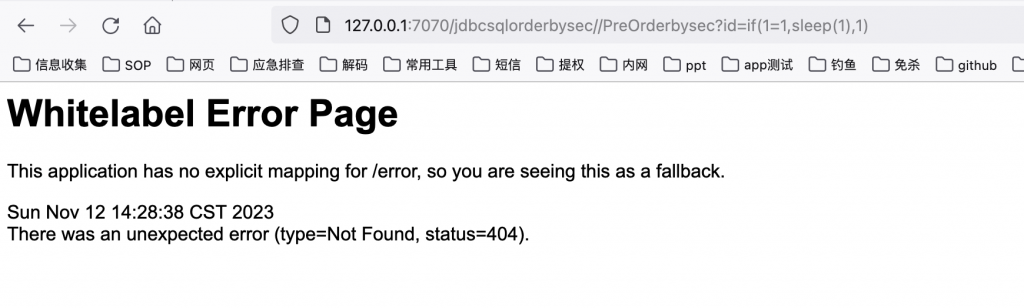
3、like注入
package com.example.sql.jdbc; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.sql.*; @RestController @RequestMapping("/jdbcsqllike") public class jdbcsqllike { private static String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; @Value("${spring.datasource.url}") private String url; @Value("${spring.datasource.username}") private String user_name; @Value("${spring.datasource.password}") private String password; @RequestMapping("/vul") public String jdbclike(@RequestParam("id") String id) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); Class.forName(driver); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user_name, password); // Vulnerable code using concatenated string String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE user_name LIKE '%" + id + "%'"; PreparedStatement preparestatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ResultSet rs = preparestatement.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { String reUsername = rs.getString("user_name"); String resPassword = rs.getString("password"); String info = String.format("%s: %s\n", reUsername, resPassword); result.append(info); } rs.close(); conn.close(); return result.toString(); } }
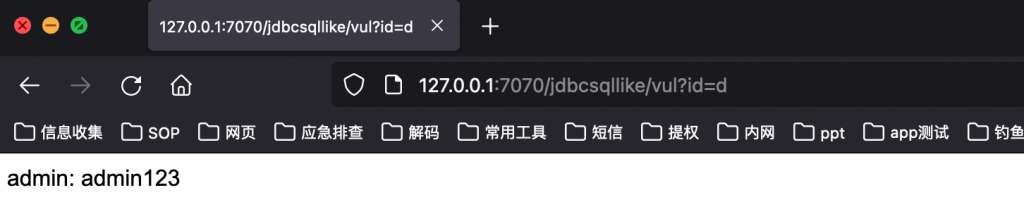
测试
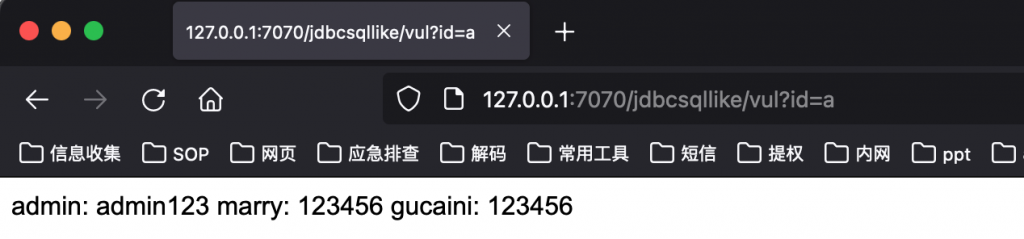
http://127.0.0.1:7070/jdbcsqllike/vul?id=d
http://127.0.0.1:7070/jdbcsqllike/vul?id=a
漏洞修复
package com.example.sql.jdbc;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.sql.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/jdbcsqllikesec")
public class jdbcsqllikesec {
private static String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String user_name;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
@RequestMapping("/secure")
public String jdbclikeSecure(@RequestParam("id") String id) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user_name, password)) {
// Secure code using parameterized query
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE user_name LIKE ?";
try (PreparedStatement preparestatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparestatement.setString(1, "%" + id + "%");
ResultSet rs = preparestatement.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String reUsername = rs.getString("user_name");
String resPassword = rs.getString("password");
String info = String.format("%s: %s\n", reUsername, resPassword);
result.append(info);
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); // Log or handle the exception appropriately
return "Error occurred: " + e.getMessage();
}
return result.toString();
}
}
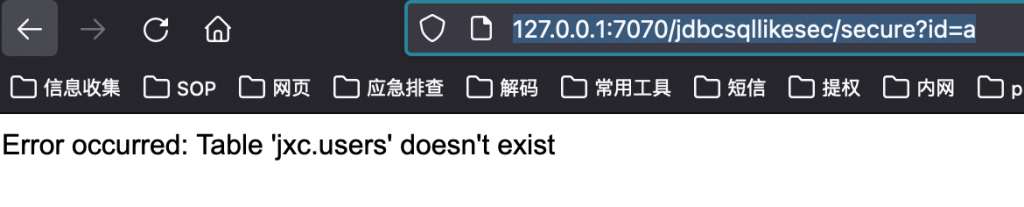
http://127.0.0.1:7070/jdbcsqllikesec/secure?id=a
(二)、Mybatis的SQL注入
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 免除了几乎 所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映 射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
在Mybatis中拼接SQL语句有两种方式:一种是占位符 #{} ,另一种是拼接符 ${} 。
占位符 #{} :对传入的参数进行预编译转义处理。类似JDBC中的 PreparedStatement 。
拼接符 ${} :对传入的参数不做处理,直接拼接,进而会造成SQL注入漏洞。
#{} 可以有效防止SQL注入漏洞。 ${} 则无法防止SQL注入漏洞。 因此在我们对JavaWeb整合Mybatis系统进行代码审计时,应着重审计SQL语句拼接的地方。 除非开发人员的粗心对拼接语句使用了 ${} 方式造成的SQL注入漏洞。
在Mybatis中有几种场景是不能使用预编译方式的,比如: order by 、 in , like 。
1、${}和#{}
在MyBatis中,${}和#{}都用于在SQL语句中进行参数替换,但它们的工作方式不同,对于SQL注入有不同的影响。
-
${}(字符串替换):- 在MyBatis中,
${}用于简单的字符串替换。参数的值直接插入到SQL语句中,没有额外的处理。 - 如果输入没有得到适当的验证或清理,这可能导致SQL注入。
<!-- 使用 ${} 的示例 --> <select id="getUserById" resultType="User"> SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ${userId} </select> - 在MyBatis中,
如果 userId 没有得到适当的验证,攻击者可以提供一个值来修改查询,从而导致SQL注入。
// Java代码中的使用示例
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("userId", "1 OR 1=1");
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("getUserById", paramMap);
-
在这个例子中,如果
userId没有得到适当的验证,它可能导致SQL注入,查询变为SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1 OR 1=1,这将总是返回结果。 -
#{}(预处理语句):- 在MyBatis中,
#{}用于预处理语句中的参数替换。MyBatis会处理值,确保它们被适当地转义和清理。 #{}比${}更安全,有助于防止SQL注入。
<!-- 使用 #{} 的示例 --> <select id="getUserById" resultType="User"> SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = #{userId} </select> - 在MyBatis中,
// Java代码中的使用示例
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("userId", "1 OR 1=1");
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("getUserById", paramMap);
-
在这种情况下,MyBatis将以一种防止SQL注入的方式处理参数替换,生成的查询将是
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?。
总结:
- 尽可能使用
#{}进行参数替换,以防止SQL注入。MyBatis会处理这些值,确保它们被适当地转义。 - 避免使用
${},除非你确信输入已经得到适当的验证和清理,因为它会直接替换值到SQL语句中。
在使用用户输入时,请谨慎对待并在将其用于SQL语句之前验证/清理它们,以防止安全漏洞,如SQL注入。
mybatis中有些地方不能使用预编译的,这种场景下就容易出现sql注入漏洞:
动态 SQL 中的表名、列名:如果在动态 SQL 中使用 ${} 来表示表名、列名等标识符,因为这些标识符是在 SQL 解析阶段确定的,无法使用预编译参数来替换。
动态 SQL 中的 SQL 语句片段:例如在 <sql> 或 <selectKey> 等元素中使用 ${},这些片段是在 SQL 解析阶段确定的,也无法使用预编译参数来替换。
动态 SQL 中的 ORDER BY 字段:如果在 ORDER BY 子句中使用 ${} 来表示排序字段,因为排序字段是在 SQL 解析阶段确定的,同样无法使用预编译参数来替换。
LIKE 操作中的模糊查询字符串:如果在 LIKE 操作中使用 ${} 来表示模糊查询的字符串,因为这个字符串是直接拼接到 SQL 语句中的,不会被预编译。
2、orderby 注入
在 MyBatis 中,Order By 注入是一种常见的 SQL 注入攻击类型。这种攻击通常发生在使用动态 SQL 语句时,特别是当使用字符串拼接来构建 Order By 子句时。为了防止 Order By 注入,我们通常建议使用 #{} 来处理动态参数。
假设有一个 MyBatis 映射文件,其中有一个动态 SQL 语句用于构建 Order By 子句:
// 由于使用#{}会将对象转成字符串,形成order by "user" desc造成错误,因此很多研发会采用${}来解决,从而造成SQL注入
@GetMapping("/vul/order")
public List<User> orderBy(String field, String sort) {
return userMapper.orderBy(field, sort);
}
// xml方式
<select id="orderBy" resultType="com.best.hello.entity.User">
select * from users order by ${field} ${sort}
</select>
// 注解方式
@Select("select * from users order by ${field} desc")
List<User> orderBy2(@Param("field") String field);
漏洞修复- 排序映射
<select id="orderBySafe" resultType="com.best.hello.entity.User">
select * from users
<choose>
<when test="field == 'id'">
order by id desc
</when>
<when test="field == 'user'">
order by user desc
</when>
<otherwise>
order by id desc
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
3、like注入
<select id="list" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Emp">
select *
from emp
<where>
<if test="name!=null and name!=''">
name like '% $iname} %'
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">
gender = #{gender}
</if>
<if test="begin!=null and end!=null">
entrydate between #{begin} and #{end}
</if>
</where>
order by update_time desc
</select>
安全写法:使用concat将%%与预编译组合起来。
<select id="list" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Emp">
select *
from emp
<where>
<if test="name!=null and name!=''">
name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">
gender = #{gender}
</if>
<if test="begin!=null and end!=null">
entrydate between #{begin} and #{end}
</if>
</where>
order by update _time desc
</select>




![[免费资源]小迪安全2023全套课程+相关资料-隼目安全](https://www.cn-fnst.top/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/ad1a1b718320240711191244-300x210.png)




暂无评论内容